Post Content
Definition:
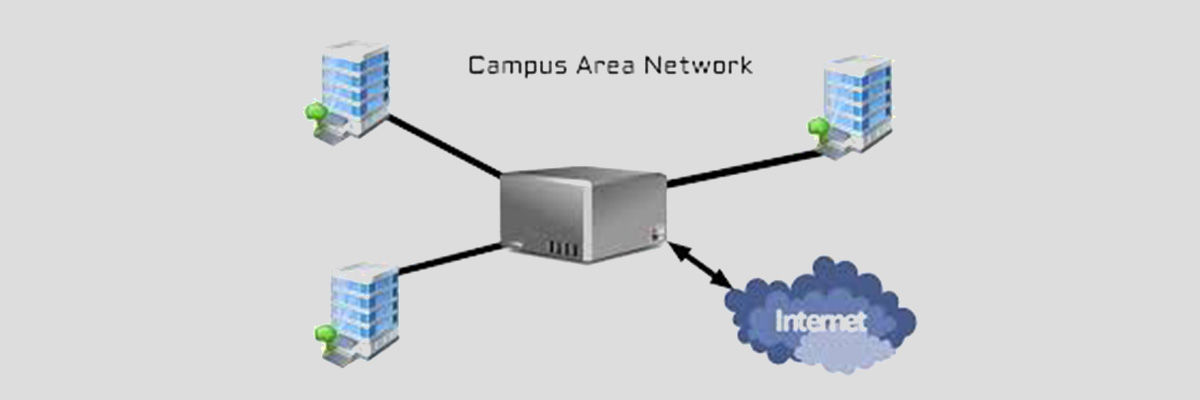
A Campus Area Network (CAN) is a network that connects multiple LANs within a limited geographical area, such as a university campus, a business park, or a large office complex. It typically covers a larger area than a LAN but is smaller than a WAN.
Key Features:
- Medium Coverage: CAN typically spans a few kilometers, covering an entire campus or a group of buildings.
- High Speed: CANs provide fast data transfer rates similar to LANs, making them suitable for large-scale data sharing.
- Cost-Effective: The cost of setting up and maintaining a CAN is generally higher than a LAN but lower than a WAN.
- Centralized Management: It allows centralized management of resources and services across multiple buildings or locations within the same area.
Core Components:
- Switches: Used to connect devices and manage network traffic within the campus.
- Routers: Connect the CAN to external networks, such as the internet or other remote sites.
- Cabling or Wireless Infrastructure: Can include fiber optics, Ethernet cables, or wireless access points.
Uses:
- Connecting multiple buildings or departments within a university or large organization.
- Sharing resources like files, printers, and applications across the campus.
- Facilitating communication between devices in a large office or educational institution.
Example:
A university might use a CAN to connect various buildings, such as classrooms, libraries, and dormitories, allowing students and faculty to access shared resources like the internet, files, and applications.
Summary:
A Campus Area Network (CAN) is a network designed to connect multiple LANs within a larger area, such as a university campus or a business complex, providing high-speed communication and resource sharing over a moderate geographic area.


Share Post For Social Media