Post Content
Definition:
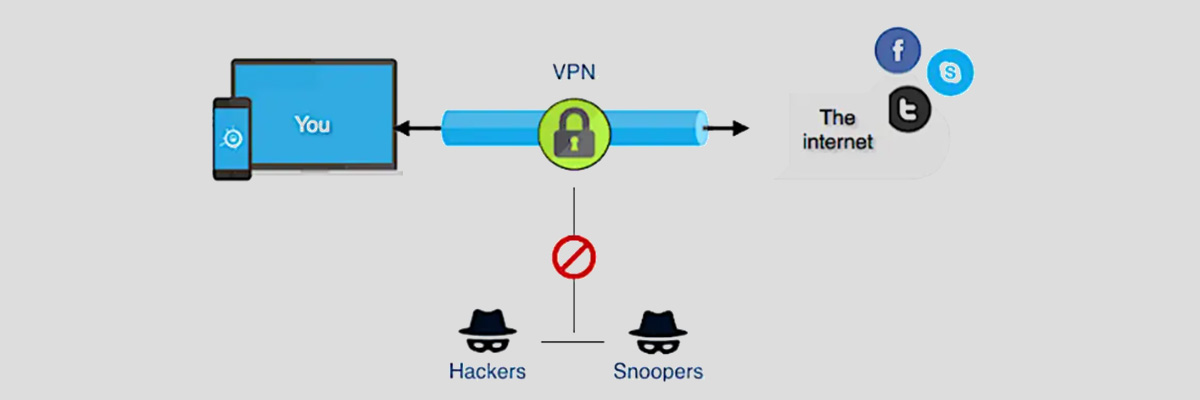
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection over a public network (like the internet), allowing users to send and receive data as if their devices were directly connected to a private network.
Key Features:
- Security: VPNs encrypt data, protecting it from hackers or unauthorized access, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Privacy: VPNs mask your IP address, helping to protect your online privacy by hiding your actual location and browsing activities.
- Remote Access: VPNs enable users to access a private network (like a company’s internal network) from remote locations as if they were physically on-site.
- Bypass Restrictions: VPNs allow users to bypass geo-restrictions or censorship by connecting to servers in different countries.
Core Components:
- VPN Client: Software installed on the user’s device to connect to the VPN.
- VPN Server: A remote server that the user’s device connects to, providing access to the private network.
- Encryption Protocols: Technologies like OpenVPN, IKEv2, or IPSec that secure the data.
Uses:
- Securely accessing sensitive data or corporate networks while working remotely.
- Protecting personal data when browsing the internet, especially on unsecured networks like public Wi-Fi.
- Circumventing government or regional internet restrictions to access websites or services from other locations.
Example:
An employee working from home can use a VPN to securely access the company’s internal systems, as if they were in the office.
Summary:
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates a secure, encrypted tunnel over the internet, enabling users to protect their data, maintain privacy, and access remote networks safely. It’s commonly used for secure internet browsing and remote access to private networks.


Share Post For Social Media